
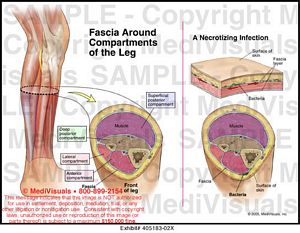
Athletes may be asked to run to reproduce the pain. X-rays and MRI studies may be ordered to exclude other causes of lower leg pain, but will be normal in CECS. Some athletes may even feel like their foot is heavy or slaps the ground firmly while running.Ī sports medicine physician will examine the athlete’s legs, which will likely appear normal. Athletes also may develop a squeezing sensation over the involved compartment, and may experience numbness, tingling, and/or burning in the lower leg and foot. If athletes do not stop exercising and try to push through the discomfort, the pain will increase in severity. With each workout, the leg pain returns at the same time in the exercise routine. If athletes stop and rest, the pain gradually goes away. It is more common in running sports, basketball, gymnastics, soccer, field hockey, and dance.ĬECS causes a dull or crampy lower leg pain which starts at some point during exercise. Men and women athletes are equally affected by the problem. This results in pain in the compartment, as well as pain or tingling in the area of the lower leg supplied by the compartment’s nerves. However, if the fascial wall of a compartment is too tight, blood flow may be cut off to the nerves and muscles. During exercise, muscles swell and fluid enters the compartment spaces. The compartments contain muscles, nerves, and blood vessels. Each compartment has a wall that is surrounded by “fascia,” a thin layer of tissue that surrounds muscles. There are four compartments in the lower leg. Chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS) is one cause of exercise-related lower leg pain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
